Herpes
Herpes: forms of infection, causes and natural treatments
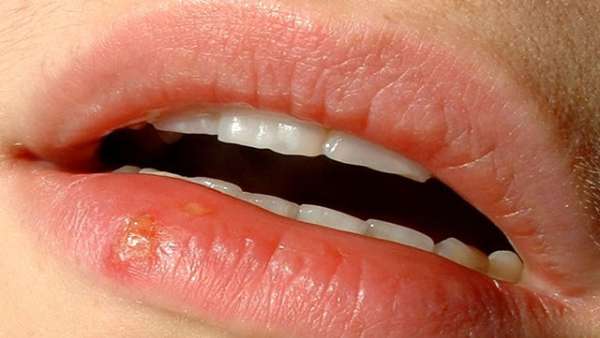
Herpes simplex virus is responsible for infections characterized by watery and painful swellings on the skin. With manifestations in two forms (oral or genital), the infection is extremely contagious, especially during the rash. HSV disease does not cure and will recur constantly, once the virus is contracted, having a very high frequency of infection, with multiple reactivations during life.
Extremely common, herpes is found in most adults, in a huge proportion globally. Infections with the two types of Herpes simplex virus (which are part of the Herpesviridae family and cause acute and recurrent infections) are present all over the globe and because the transmission is made from one person to another, through direct contact with fluids or secretions. From a medical point of view, the manifestations include rash and severe itching, difficult to control. As a localization, herpes can occur both in the mouth or face and in the genital area.
Herpes simplex type 1 (HSV 1, orofacial herpes, the most common), respectively herpes simplex type 2 (HSV 2, genital herpes, asymptomatic in nature) are the main forms.
With an incubation period ranging from 4-12 days after exposure, the virus can then begin to develop painful ulcers and recovery periods range from 2 to 4 weeks. However, most of the time, the virus remains unnoticed, with no manifestations. If the virus has reached the body once, it remains a carrier for the rest of its life, reactivating periodically.
The main impediment remains the impact on personal life, especially relationships with the partner, all people being susceptible to herpes virus infection. The virus can be kept under control in clinically healthy people, but can be threatening to people with weakened immune systems or pregnant women. Fortunately, the lesions can be alleviated either by medication prescribed by a specialist or by natural remedies used at home.
Symptoms of herpes virus infection
Once the herpes virus reaches the body, it often has common manifestations for the affected area, orally or genitally. It varies in active cycles of the disease, followed by asymptomatic periods, which decrease in intensity over time. Unfortunately, the virus does not disappear from the body, and often herpes manifestations do not exist, but the virus remains dormant until it attacks again, when the host's immune system is weakened.
Relapses can occur up to 6 times / year and symptoms include:
- the first episodes may include sharp and uncontrollable pain, fever, muscle aches, inflammation of the surrounding lymph nodes (lymph or groin), general condition affected, fatigue, lack of appetite;
- tingling and pain when urinating, wounds, increased vaginal secretions, pustules;
- numbness;
- burn or sting sensations;
- the appearance of rashes on the lips or genitals;
- severe pruritus, which is difficult to control;
- the impression of tingling or the sensation of heat in the affected area;
- very rarely, headaches and myalgia may occur.
Types of herpes
Herpes is an infection manifested on the skin and the herpes virus is part of the Herpersviridae family. HSV 1 tends to cause damage above the waist and HSV 2 tends to cause damage below the waist, both viruses affect the body and can cause the following types of conditions:
- oral herpes (on the lips, around the lips, rarely in the oral cavity);
- genital herpes (vulva, vagina, cervix, penis, perianal or anal regions);
- herpes keratitis (occurs when the eyes are affected, giving especially the feeling of "sand in the eyes");
- herpetic panaritis (occurs when the herpes infection is located on the fingernail);
- herpes gladiatorum (occurs when the head, torso and extremities may have skin lesions);
- primary herpes stomatitis (a form of infection found especially in children aged 1-3 years).
Risk factors
Herpes simplex infections are transmitted through direct contact, but there are certain risk factors that can promote the disease:
- the presence of other sexually transmitted diseases;
- an increased number of sexual partners and casual sexual contact;
- trauma to the affected or adjacent area (epilation, lip injections etc.);
- fatigue;
- organ transplant;
- immunosuppressive treatments;
- deficient immune system;
- touching the skin of an infected person;
- sharing toothbrushes or cutlery.
Triggers
Among triggers (which can cause both reactivation and primary infection) we can list:
- fatigue and stress;
- prolonged exposure to wind, sun or low temperatures (burns caused by wind, ultraviolet radiation);
- hormonal changes;
- menstruation;
- recurrent disease;
- over-cooling or over-heating of the body;
- various psycho-emotional states or physiological disorders;
- surgery;
- stomach problems or gastrointestinal disorders;
- over-excitation of the body;
- minor infections;
- the presence of a second virus in the body;
- some allergic reactions.
Complications of herpes
Herpes can become responsible for several complications, including:
- encephalitis or herpetic keratitis (occurs in immunologically compromised people, when the brain is affected);
- the virus can spread to other organs (lungs, digestive system etc.);
- severe outbreaks of herpes in people with low immunity;
- lethal herpes pneumonia, in case of patients with extensive burns;
- meningism or aseptic meningitis;
- facilitating infection with other sexually transmitted diseases;
- esophagitis;
- hepatitis;
- pneumonia;
- pneumonie;
- retinal necrosis;
- neonatal herpes, which is transmitted during birth (not after), from the mother suffering from genital herpes, to the fetus, which can be subject to severe neurological consequences, which can be life threatening;
- stigma with psychological and social impact, which negatively changes the quality of life and sexual relations.
When do I have to go to the doctor?
Although, once acquired, this virus remains in the body forever, herpes ulcers disappear on their own after about 2 weeks. In principle, a visit to a doctor is required as soon as signs are observed that may indicate the presence of herpes, but also if the symptoms do not improve after the established period or after following a prescribed treatment.
Herpes treatments
There is no definitive cure for herpes or herpes simplex virus, because it remains in the body and is activated occasionally. However, there are various treatments that can reduce the intensity of the manifestations and these can be:
Medical treatment
Which depends on the evolution over time of herpes lesions or whether you try to prevent future recurrences. There are various options that can reduce the severity and duration of the condition:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- painkillers (prescribed for pain);
- drugs that inhibit viral multiplication by blocking DNA polymerase;
- medicines that act on HSV enzymes;
- topical creams or ointments (with or without a prescription);
- antiviral medicines (with prescription only), available as pills or injections (the most indicated chemotherapeutics are acyclovir, famciclovir, valaciclovir).
Alternative medicine or complementary treatments, which may reduce symptoms:
- acupuncture (stinging of certain points located on the skin, which are located along energy meridians);
- reflexology;
- applications with polarized light;
- homeopathic treatments.
Ambulatory treatment (made at home):
- applying a damp towel on the lesions 3 times / day, for 20 minutes;
- avoid foods that contain acid;
- hot water baths;
- warm compresses to be applied as soon as the first signs appear;
- cold compresses;
- avoid wearing tight clothes around the affected area;
- application of ointments or powders with a calming effect.
Natural treatments:
- marjoram oil (local applications directly on herpes, until healing);
- propolis tincture (put on the affected area, 3-4 times / day);
- marigold infusion (1 tablespoon of plant to 300 ml of boiling water, consumed in the form of tea, 3 cups / day);
- aloe vera gel dries herpes, has a calming effect and moisturizes the area it will fade;
- garlic has antiviral properties and is used with caution in the fight against herpes (1 crushed dog, rubbed with olive oil, applied 3 times / day, on the affected area);
- a paste of baking soda and water (applied to herpes and allowed to dry) will relieve the itching;
- a cornstarch paste can also help (a mixture of starch and water is applied to the area of herpes in the evening, to act during the night and let it dry);
- honey has antibacterial properties, so put on herpes (and left on for 5-7 minutes) will relieve symptoms and also work as a sedative;
- an oily capsule of Vitamin E will relieve inflammation and pain, through its anti-inflammatory properties;
- cotton wool soaked in milk can be applied regularly on the affected areas (the content of lysine and arginine helps to improve the herpes outbreak);
- a pinch of salt can also help (put on a damp finger and held on the lesion, by pressing, for 2 minutes; at the end, the area is cleaned with cotton wool soaked in warm water);
- rich in antioxidants, the olive oil is heated a little and mixed with drops of lavender oil and beeswax (until it melts) and the mixture will be used on the affected areas;
- black tea, through its tannin content, provides antiviral and anti-inflammatory benefits; an envelope of black tea (left after the tea is made) will be left to act for 5 minutes on the herpes lesion; for more efficient results, repeat the procedure 2-3 times a day;
- apple cider vinegar can give tingling sensations, when applied on a cotton swab and then on the affected area, but it has disinfectant and astringent properties, which help in treating herpes;
- an undiluted drop of tea tree essential oil can be applied, which is a powerful antiviral and antifungal, while soothing the infected surface;
- plum juice treats wounds caused by herpes, by rinsing or in the form of a compress placed on the wounds, relieving inflammation and pain;
- black and cold coffee on wounds is a remedy that reduces herpes and will accelerate healing, by applying 2 times / day for several days.
Administration of food supplements:
- L-Lysine is an essential amino acid for tissue regeneration, recommended for people with low immunity and predisposition to herpes rashes; is a natural treatment for herpes because it prevents the reproduction of viruses;
- HerpeStop helps eliminate the unpleasant symptoms caused by the Herpes simplex virus;
- HerpEx fights herpes by relieving pain, reducing inflammation and accelerating healing, while reducing scarring and preventing unpleasant rashes;
- Ganoderma strengthens the immune system and is recommended for Herpes simplex infections;
- Thymus capsules improve the functions of the immune system, the body becoming stronger in the face of viruses;
- Artemisinin Forte is a type of herbal capsules with a strong antiviral activity against herpes;
- Echinacea tablets (Hofigal) provide the necessary bioactive substances necessary for the physiological functions of the immune system and are used to relieve the symptoms of acute or recurrent herpes infections.
Prevention of herpes infection
There are various strategies that can be adopted, both to avoid the risk of herpes infection and to avoid recurrence (which can occur at any time, once the infection has occurred). Among the changes that can be made are:
- use of lotions with sun protection factor;
- not to drink from the same glass with other people;
- do not use objects in common, which can facilitate the exchange of fluids;
- avoiding exposure to stress;
- control of agitation episodes;
- elimination of the risk of dehydration, by consuming 2 liters of fluids / day;
- not to touch the lesions, in order to avoid spreading to other areas;
- maintaining proper hygiene;
- adopting a healthy lifestyle, with adequate rest;
- keeping hands clean at all times;
- avoid salty and acidic foods, along with reducing the consumption of chocolate, peanuts, peas, seeds, oatmeal and wheat (rich in arginine, an amino acid that reactivates the virus);
- not apply cosmetics on the affected areas, in order to avoid possible irritations;
- using a condom during sexual intercourse.
Did you know that...?
- the global HSV 1 and / or HSV 2 infection rate is between 60% and 95%? The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that around 3.7 billion people under the age of 50 suffer from herpes;
- herpes has been known for at least 2,000 years? For example, Emperor Tiberius would have forbidden kissing in Rome, because many people had inflammation in their mouths;
- in the 18th century, herpes was so common among prostitutes, that it was considered “a professional disease of women?
- it was only in 1940 that it was discovered that herpes is a virus, so that only in 1960 to start an experimental antiviral treatment?
- many people who are diagnosed with genital herpes suffer from episodes of depression, isolation, fear of rejection or develop feelings of destruction? That is why there are support groups in many countries around the world, where sufferers meet and socialize;
- according to a Swedish study, if you are infected with HSV 1, your risk of Alzheimer's disease is doubled? At the same time, according to the WHO, people infected with HSV 2 are at least three times more likely to become infected with HIV if exposed to it;
- genital herpes affects women more than men, because the infection is more easily transmitted from the penis to the vagina?
- a study shows that the two types of Herpes simplex virus - HSV 1 and HSV 2 - have come to combine their genetic material, so there are more re-combinations of herpes than was known and there is a possibility that HSV 2 will evolve to become resistant to known anti-virals?
Comments