Impetigo
Impetigo / Sweet Bubes: Herbal treatments and effective remedies
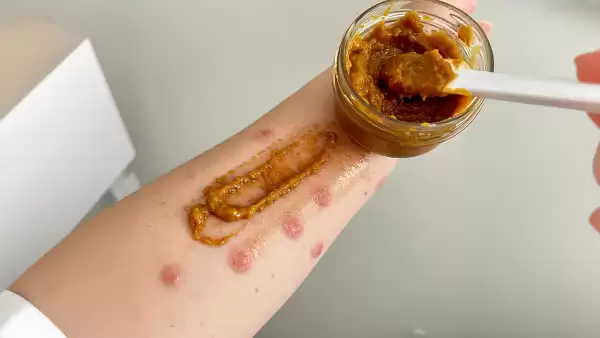
Impetigo, also popularly known as sweet itch, is a bacterial skin infection, common in children, but which can also affect adults. It causes red, gold-crusted lesions that can be painful and unsightly. Fortunately, there are many natural remedies that can help treat and prevent impetigo, using simple and effective ingredients.
What is impetigo?
Impetigo or sweet itch is a contagious bacterial skin infection caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. It mainly affects children, but can also occur in adults. The disease manifests as red lesions, which later develop yellow-brown, honey-like scabs.
Causes and risk factors
- Direct contact with an infected person
- Minor skin injuries (cuts, scratches, insect bites)
- Poor hygiene
- Excessive sweating
- Low immunity
- Hot and humid climate
Symptoms of impetigo
- Red lesions on the skin
- Golden-brown scabs
- Itching and discomfort
- Intense itching
- Local swelling
- Mild fever (in severe cases)
Complications
- Spread of infection to other skin areas
- Deeper skin infections (cellulitis)
- Kidney damage (post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis)
- Scarring
Natural remedies to treat impetigo
1. Baked carrot paste
An effective natural remedy for impetigo is ripe carrot paste, which helps skin regeneration and has antibacterial properties. Apply directly to the affected areas, leave for 20 minutes, then rinse with lukewarm water.
2. Manuka honey
Applied directly to lesions, Manuka honey has powerful antibacterial properties, accelerating healing.
3. Coconut oil
Coconut oil contains lauric acid, which fights bacteria and soothes inflammation.
4. Tea tree essential oil
Diluted with a carrier oil, it helps disinfect lesions and reduce inflammation.
5. Aloe vera
Aloe vera extract has soothing effects and accelerates skin regeneration.
6. Apple cider vinegar
A diluted solution of apple cider vinegar can be applied to reduce bacterial overgrowth.
7. Clay poultice
Clay has antiseptic properties and helps eliminate toxins. Apply a thin layer to the affected areas and leave until dry.
8. Thyme infusion
Thyme has powerful antibacterial properties. Prepare a concentrated infusion and apply to lesions with a compress.
Foods beneficial for impetigo
- Carrots - rich in beta-carotene, helps skin regeneration.
- Garlic - powerful natural antibiotic.
- Turmeric - has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Ginger - supports the immune system.
- Citrus fruits - rich in vitamin C, essential for healing.
- Green tea - natural antioxidant, reduces inflammation.
- Manuka honey - antimicrobial.
- Flaxseed - rich in omega-3 fatty acids, helps replenish skin.
Did you know...? 🤔
- Impetigo is one of the most common bacterial skin infections in children. 🧒
- The disease is more common in warm and humid climates, where bacteria spread rapidly. ☀️
- It can be spread by touching contaminated objects such as towels or toys. 🧸
- Carrots are rich in beta-carotene, which is essential for skin regeneration and boosting immunity. 🥕 S ee the baked carrot paste remedy.
- Coconut oil is an effective natural remedy due to its high lauric acid content. 🥥
- One of the oldest treatments for impetigo is Manuka honey, used for centuries for its antibacterial properties. 🍯
- Frequent hand washing significantly reduces the risk of contracting impetigo. 🧼
- A diet rich in antioxidants can help prevent recurrence of the disease. 🥦
- Aloe vera not only soothes the skin but also helps lesions heal faster. 🌿
- Green tea has anti-inflammatory effects and can support the immune system in fighting infection. 🍵
- Applying a thyme-infused compress can help to naturally disinfect the skin. 🌱
- Turmeric has a powerful antibacterial effect and helps reduce inflammation. 🟡
- Children are more prone to impetigo because they have more sensitive skin and a developing immune system. 👶
Comments